Limit on lab-grown human embryos dropped by stem-cell body
By Nidhi Subbaraman,
Nature
| 05. 26. 2021
The International Society for Stem Cell Research relaxed the famous 14-day rule on culturing human embryos in its latest research guidelines.
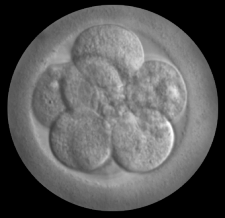
The international body representing stem-cell scientists has torn up a decades-old limit on the length of time that scientists should grow human embryos in the lab, giving more leeway to researchers who are studying human development and disease.
Previously, the International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) recommended that scientists culture human embryos for no more than two weeks after fertilization. But on 26 May, the society said it was relaxing this famous limit, known as the ‘14-day rule’. Rather than replace or extend the limit, the ISSCR now suggests that studies proposing to grow human embryos beyond the two-week mark be considered on a case-by-case basis, and be subjected to several phases of review to determine at what point the experiments must be stopped.
The ISSCR made this change and others to its guidelines for biomedical research in response to rapid advances in the field, including the ability to create embryo-like structures from human stem cells. In addition to relaxing the ‘14-day rule’, for instance, the group advises against editing genes in human embryos until the safety of genome...
Related Articles
By Scott Solomon, The MIT Press Reader | 02.12.2026
Chris Mason is a man in a hurry.
“Sometimes walking from the subway to the lab takes too long, so I’ll start running,” he told me over breakfast at a bistro near his home in Brooklyn on a crisp...
By Zachary Brennan, Endpoints News | 02.23.2026
The FDA is spelling out the details of a new pathway to help speed personalized cell and gene therapies to market for rare diseases.
Monday’s long-awaited draft guidance outlines the agency’s “plausible mechanism” framework, a pathway FDA Commissioner Marty Makary...
By Amy Feldman, Forbes | 02.17.2026
"Jennifer Doudna" by Duncan Hull for the Royal Society via Wikimedia Commons licensed under CC by SA 3.0
Soon after KJ Muldoon was born in August 2024, he was lethargic and wouldn’t eat. His worried doctors realized his ammonia...
By David Jensen, California Stem Cell Report | 02.10.2026
Touchy issues involving accusations that California’s $12 billion gene and stem cell research agency is pushing aside “good science” in favor of new priorities and preferences will be aired again in late March at a public meeting in Sacramento.
The...