Bias and Inaccuracy in Marketing Noninvasive Prenatal Tests
By Editors,
The Hastings Center
| 03. 08. 2022
Photo by Scott via wikimedia
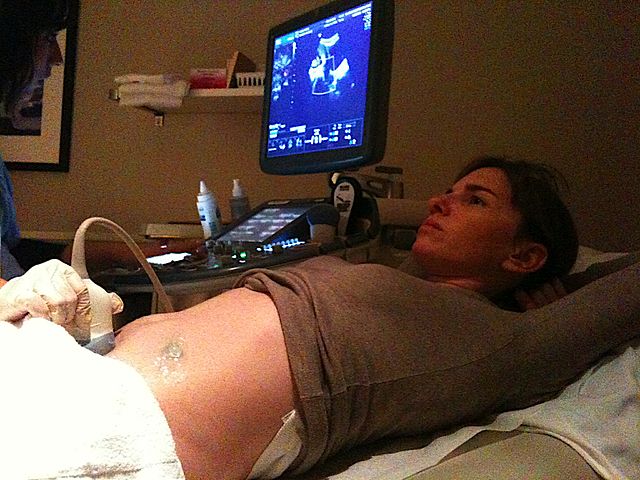
Bias and inaccuracy are pervasive in the marketing of noninvasive prenatal tests (NIPTs), concludes an early-view study in the Hastings Center Report. The tests are marketed to consumers around the world without regulatory oversight.
NIPTs are screening tests that assess the chance that a fetus is affected by various chromosomal and other conditions by analyzing fetal DNA in a maternal blood sample. In the absence of regulation, the responsibility to ensure that NIPTs are represented accurately and ethically falls to manufacturers.
The study examined whether manufacturers live up to this responsibility by evaluating English-language consumer brochures for NIPTs marketed globally. For a benchmark, the study used a guidance document produced by the Nuffield Council on Bioethics in the United Kingdom. Among the major findings:
- None of the brochures complied with all of the Council’s criteria.
- Fifty-two percent of the brochures misrepresented NIPTs as diagnostic rather than screening tests. Patients who do not understand that follow-up diagnostic testing is required to confirm a positive NIPT result may make decisions about their pregnancy, such as having...
Related Articles
By Scott Solomon, The MIT Press Reader | 02.12.2026
Chris Mason is a man in a hurry.
“Sometimes walking from the subway to the lab takes too long, so I’ll start running,” he told me over breakfast at a bistro near his home in Brooklyn on a crisp...
By Katrina Miller, The New York TImes | 02.05.2026
Joseph Yracheta: The Native Biodata Consortium is the first nonprofit data and sample repository within the geographic bounds and legal jurisdiction of an American Indian nation, on the Cheyenne River Sioux Reservation in Eagle Butte, S.D.
NativeBio participated in a ...
By David Jensen, California Stem Cell Report | 02.10.2026
Touchy issues involving accusations that California’s $12 billion gene and stem cell research agency is pushing aside “good science” in favor of new priorities and preferences will be aired again in late March at a public meeting in Sacramento.
The...
By Lauren Hammer Breslow and Vanessa Smith, Bill of Health | 01.28.2026
On Jan. 24, 2026, the New York Times reported that DNA sequences contributed by children and families to support a federal effort to understand adolescent brain development were later co-opted by other researchers and used to publish “race science”...