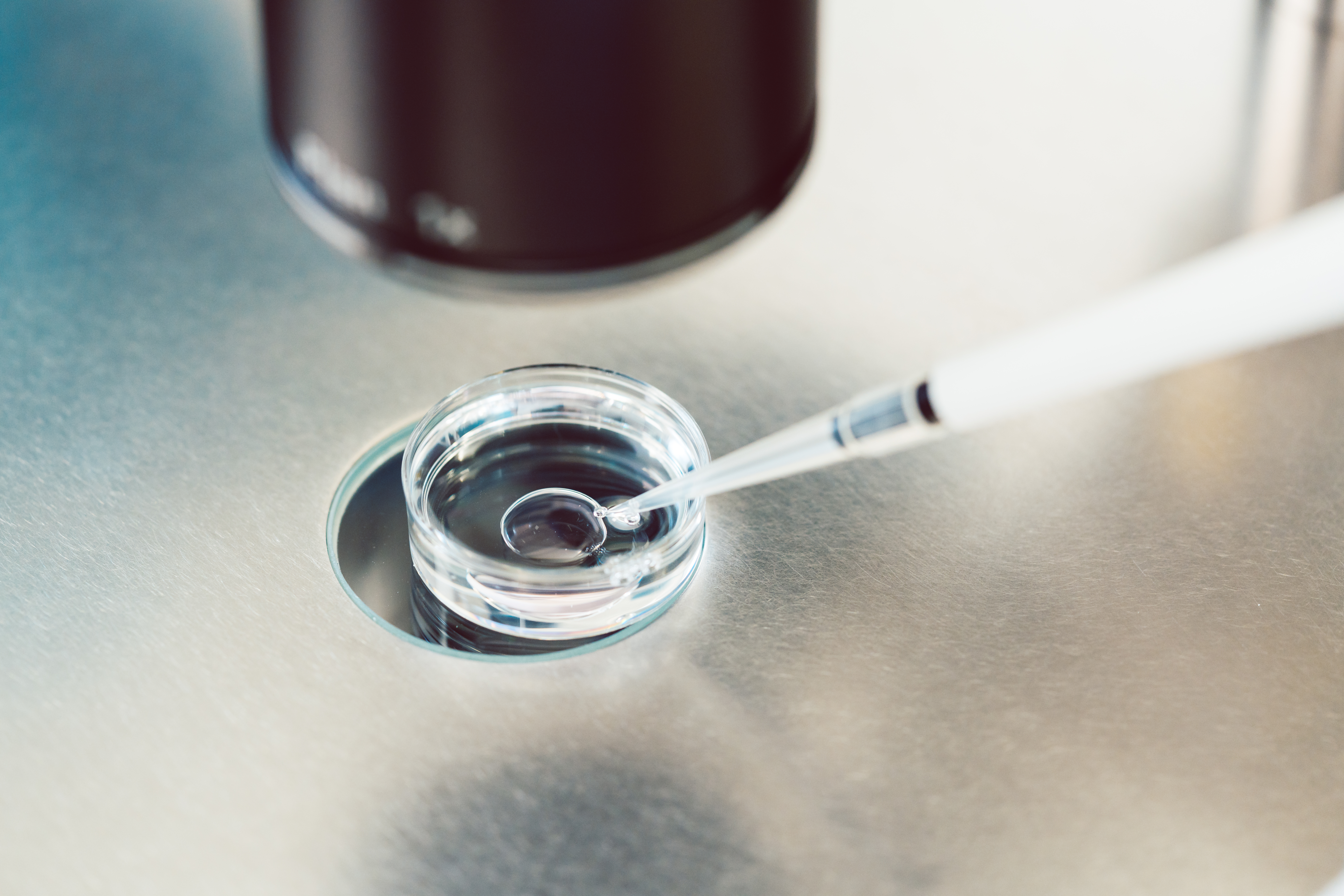
The Alabama IVF ruling uses faux scientific language to justify a religious position
By David Sable,
STAT
| 02. 22. 2024
Imagine having 15 miscarriages.
Maybe you can shrug off the first one or two and keep trying to have children, to create a family. But soon every positive pregnancy test brings a sense of dread, of sad inevitability. Your body becomes your enemy.
In 1998, my group at Saint Barnabas Medical Center in suburban New Jersey was part of a team that developed a way to test for a genetic variant called a translocation, a swapping of parts of one chromosome with a different chromosome. For the most part, people with genetic translocations are completely fine; they have all of the same genes as anyone else. The problems arises when their cells have to split their chromosomes to make eggs or sperm, most of which have too much or little of some of the translocated genes. These unbalanced sperm and eggs create unbalanced embryos, which rarely develop past the second trimester.
By using fertility drugs to mature a number of eggs at once and fertilizing all of them, my colleagues and I were able to identify the small number of...
Related Articles
By Jenn White, NPR | 02.26.2026
By Vittoria Vardanega, SWI swissinfo.ch | 02.13.2026
In recent years, sperm donation has produced family trees of unprecedented size, stretching across countries and, in some cases, continents. Stories of “mass donors” have captured public attention, most recently through the Netflix documentary series, The Man with 1,000 Kids...
By Ava Kofman, The New Yorker | 02.09.2026
1. The Surrogates
In the delicate jargon of the fertility industry, a woman who carries a child for someone else is said to be going on a “journey.” Kayla Elliott began hers in February, 2024, not long after she posted...
By Alex Polyakov, The Conversation | 02.09.2026
Prospective parents are being marketed genetic tests that claim to predict which IVF embryo will grow into the tallest, smartest or healthiest child.
But these tests cannot deliver what they promise. The benefits are likely minimal, while the risks to...