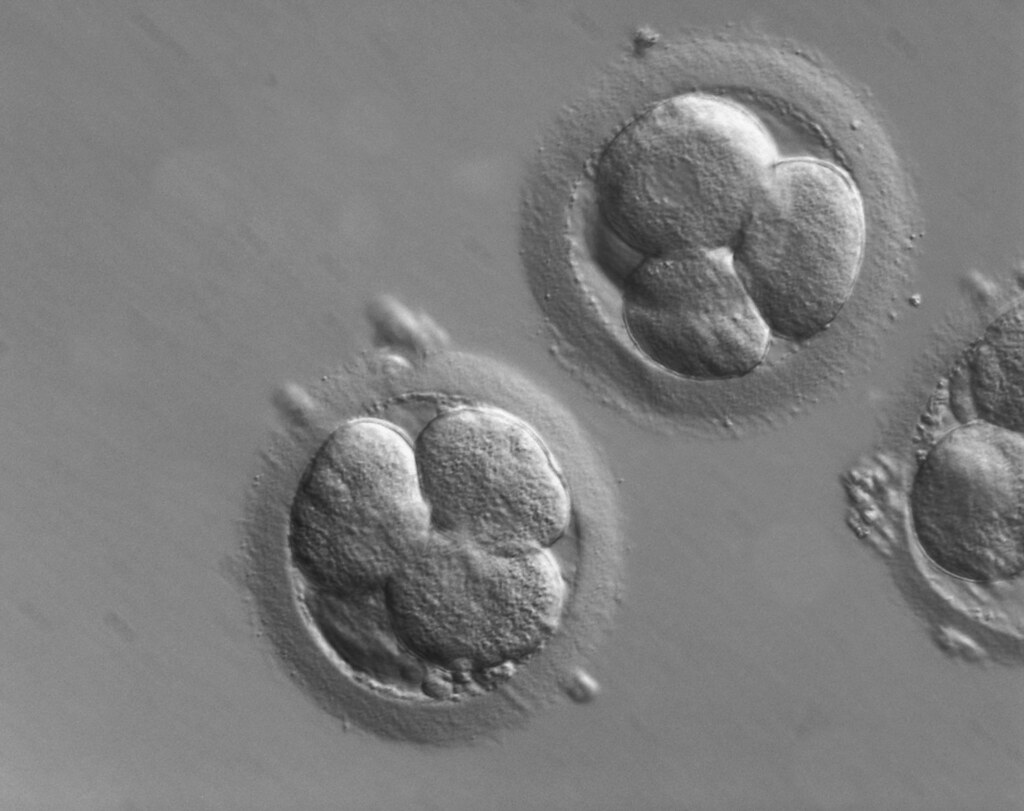
Scientists say they can read nearly the whole genome of an IVF-created embryo
By Jennifer Couzin-Frankel,
Science
| 03. 21. 2022
Photo by ZEISS Microscopy on Flickr
A California company says it can decipher almost all the DNA code of a days-old embryo created through in vitro fertilization (IVF)—a challenging feat because of the tiny volume of genetic material available for analysis. The advance depends on fully sequencing both parents’ DNA and “reconstructing” an embryo’s genome with the help of those data. And the company suggests it could make it possible to forecast risk for common diseases that develop decades down the line. Currently, such genetic risk prediction is being tested in adults, and sometimes offered clinically. The idea of applying it to IVF embryos has generated intense scientific and ethical controversy. But that hasn’t stopped the technology from galloping ahead.
Heart conditions, autoimmune diseases, cancer, and many other adult ailments have complex and often mysterious origins, fueled by a mix of genetic and environmental influences. Hundreds of variations in the human genome can collectively raise or lower risk of a particular disease, sometimes by a lot. Predicting a person’s chance of a specific illness by blending this genetic variability into...
Related Articles
By Scott Solomon, The MIT Press Reader | 02.12.2026
Chris Mason is a man in a hurry.
“Sometimes walking from the subway to the lab takes too long, so I’ll start running,” he told me over breakfast at a bistro near his home in Brooklyn on a crisp...
By Diaa Hadid and Shweta Desai, NPR | 01.29.2026
MUMBRA, India — The afternoon sun shines on the woman in a commuter-town café, highlighting her almond-shaped eyes and pale skin, a look often sought after by couples who need an egg to have a baby.
"I have good eggs,"...
By George Janes, BioNews | 01.12.2026
A heart attack patient has become the first person to be treated in a clinical trial of an experimental gene therapy, which aims to strengthen blood vessels after coronary bypass surgery.
Coronary artery bypass surgery is performed to treat...
By Staff, ScienceDaily | 01.05.2026
Scientists at UNSW Sydney have developed a new form of CRISPR technology that could make gene therapy safer while also resolving a decades-long debate about how genes are switched off. The research shows that small chemical markers attached to DNA
...