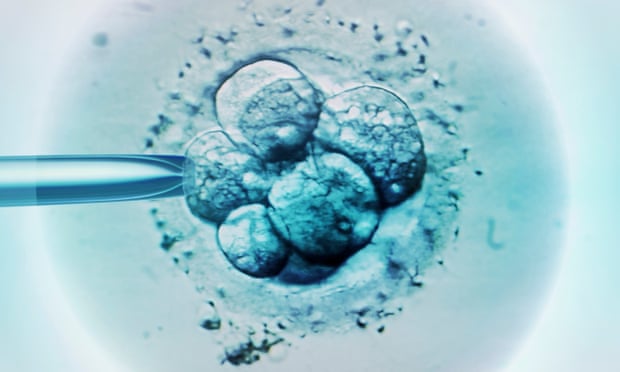
Russian ‘CRISPR-Baby’ Scientist has Started Editing Genes in Human Eggs with Goal of Altering Deaf Gene
By David Cyranoski,
Nature
| 10. 18. 2019
Russian biologist Denis Rebrikov has started gene editing in eggs donated by women who can hear to learn how to allow some deaf couples to give birth to children without a genetic mutation that impairs hearing. The news, detailed in an e-mail he sent to Nature on 17 October, is the latest in a saga that kicked off in June, when Rebrikov told Nature of his controversial intention to create gene-edited babies resistant to HIV using the popular CRISPR tool.
Rebrikov’s latest e-mail (see box) follows a September report in Russian magazine N+1 that one deaf couple had started procedures to procure eggs that would be used to create a gene-edited baby — but the eggs that Rebrikov has edited are from women without the genetic mutation that can impair hearing. He says the goal of the experiments is to better understand potentially harmful ‘off-target’ mutations, which are a known challenge of using CRISPR–Cas9 to edit embryos.
In his e-mail to Nature, Rebrikov makes clear that he does not plan to create such a baby yet — and that his...
Related Articles
By Diaa Hadid and Shweta Desai, NPR | 01.29.2026
MUMBRA, India — The afternoon sun shines on the woman in a commuter-town café, highlighting her almond-shaped eyes and pale skin, a look often sought after by couples who need an egg to have a baby.
"I have good eggs,"...
By George Janes, BioNews | 01.12.2026
A heart attack patient has become the first person to be treated in a clinical trial of an experimental gene therapy, which aims to strengthen blood vessels after coronary bypass surgery.
Coronary artery bypass surgery is performed to treat...
By Staff, ScienceDaily | 01.05.2026
Scientists at UNSW Sydney have developed a new form of CRISPR technology that could make gene therapy safer while also resolving a decades-long debate about how genes are switched off. The research shows that small chemical markers attached to DNA
...
Following a long-standing CGS tradition, we present a selection of our favorite Biopolitical Times posts of the past year.
In 2025, we published up to four posts every month, written by 12 authors (staff, consultants and allies), some in collaboration and one simply credited to CGS.
These titles are presented in chronological order, except for three In Memoriam notices, which follow. Many more posts that are worth your time can be found in the archive. Scroll down and “VIEW...