Is Reducing Down Syndrome Births a Form of Eugenics?
By Richard Gunderman,
Psychology Today
| 01. 03. 2021
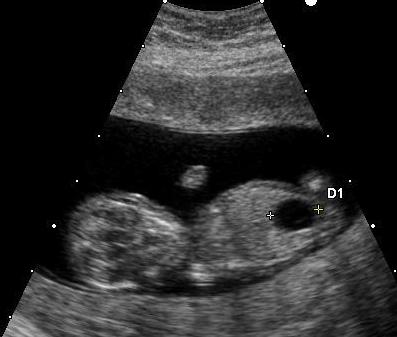
A recently released study finds that Europe has reduced the number of babies born with Down syndrome by 54%. In 2016, the same researchers found that the U.S. rate of Down syndrome births had declined by 33%. Some friends and colleagues have asked me whether such reductions, which entail prenatal diagnosis and elective pregnancy termination, mean that we are still practicing some form of eugenics.
Down syndrome is a genetic disorder usually associated with an extra copy of chromosome 21 – hence its other name, trisomy 21. Children with Down syndrome generally exhibit growth delays, reduced intelligence, and a shortened life span of around 60 years. The risk of having a baby with Down syndrome increases with parental age. When prenatal testing reveals the diagnosis, some parents, including apparently many in Europe and the US, elect to terminate the pregnancy.
The widely-shared belief that people with Down syndrome cannot have children is mistaken. Fertility rates across the board for individuals with Down syndrome are lower – and much lower in men than in women – but babies have been...
Related Articles
By Kiana Jackson and Shannon Stubblefield, New Disabled South | 02.09.2026
"MC0_8230" via Wikimedia Commons licensed under CC by 2.0
This report documents a deliberate assault on disabled people in the United States. Not an accident. Not a series of bureaucratic missteps. An assault that has been coordinated across agencies...
By Scott Solomon, The MIT Press Reader | 02.12.2026
Chris Mason is a man in a hurry.
“Sometimes walking from the subway to the lab takes too long, so I’ll start running,” he told me over breakfast at a bistro near his home in Brooklyn on a crisp...
By Jonathan D. Moreno, Hastings Center Bioethics Forum | 02.09.2026
When I began to write a book about bioethics and the rules-based international order, the idea that the world was facing the greatest geopolitical change since World War II was uncontroversial for those who were paying attention to such esoterica...
By Amy Feldman, Forbes | 02.17.2026
"Jennifer Doudna" by Duncan Hull for the Royal Society via Wikimedia Commons licensed under CC by SA 3.0
Soon after KJ Muldoon was born in August 2024, he was lethargic and wouldn’t eat. His worried doctors realized his ammonia...