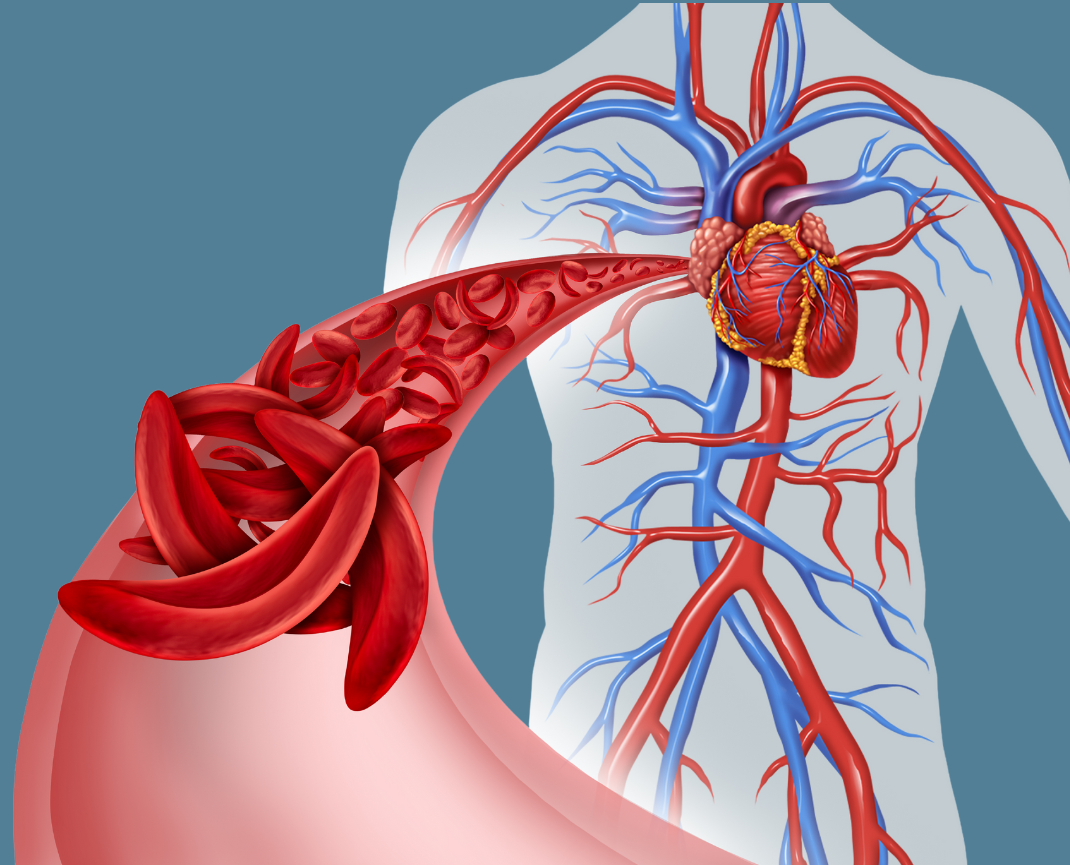
New way for states to cover pricey gene therapies will start with sickle cell disease
By Nada Hassanein,
New Jersey Monitor
| 03. 14. 2024
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration late last year approved two breakthrough gene therapies for sickle cell disease patients. Now a new federal program seeks to make these life-changing treatments available to patients with low incomes — and it could be a model to help states pay for other expensive therapies.
The new sickle cell treatments have brought hope to those with the debilitating blood disorder, which is hereditary and disproportionately affects Black people. But the therapies come with a price tag of as much as $3 million for a course of treatment, which can take up to a year. Despite those high upfront costs, cell and gene therapies have the potential to reduce health care spending over time by addressing the underlying cause of the disease.
Under the so-called Cell and Gene Therapy Access Model, the federal government will negotiate discounts with sickle cell drug manufacturers Vertex Pharmaceuticals, CRISPR Therapeutics and Bluebird Bio on behalf of state Medicaid agencies, which provide health care coverage to low-income patients. To participate, state Medicaid agencies must agree to prices based on those negotiations...
Related Articles
By Scott Solomon, The MIT Press Reader | 02.12.2026
Chris Mason is a man in a hurry.
“Sometimes walking from the subway to the lab takes too long, so I’ll start running,” he told me over breakfast at a bistro near his home in Brooklyn on a crisp...
By Zachary Brennan, Endpoints News | 02.23.2026
The FDA is spelling out the details of a new pathway to help speed personalized cell and gene therapies to market for rare diseases.
Monday’s long-awaited draft guidance outlines the agency’s “plausible mechanism” framework, a pathway FDA Commissioner Marty Makary...
By Amy Feldman, Forbes | 02.17.2026
"Jennifer Doudna" by Duncan Hull for the Royal Society via Wikimedia Commons licensed under CC by SA 3.0
Soon after KJ Muldoon was born in August 2024, he was lethargic and wouldn’t eat. His worried doctors realized his ammonia...
By David Jensen, California Stem Cell Report | 02.10.2026
Touchy issues involving accusations that California’s $12 billion gene and stem cell research agency is pushing aside “good science” in favor of new priorities and preferences will be aired again in late March at a public meeting in Sacramento.
The...