How stress echoes down the generations
By The Economist,
The Economist
| 05. 24. 2018
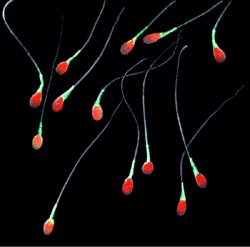
The effects of child abuse can last a lifetime. Neglected or abused children have a higher risk of developing all sorts of ailments as adults, including mental illnesses such as depression but also physical ones like cancer and stroke. In fact, the effects may last even longer. Emerging evidence suggests that the consequences of mistreatment in childhood may persist down the generations, affecting a victim’s children or grand-children, even if they have experienced no abuse themselves.
Exactly how this happens is not well understood. Rigorous experiments on human subjects are difficult. Scientists have therefore turned to rats and mice. But now Larry Feig of Tufts University and his colleagues have shown that psychological stress seems to cause similar changes in the sperm of both mice and men. Their study is published this week in Translational Psychiatry.
Biologists know that traits are carried down the generations by genes. Genes encode proteins, and proteins make up organisms. That is still true. But it has recently become clear that it is not the whole story. Organisms regulate the activity of their genes throughout...
Related Articles
By Scott Solomon, The MIT Press Reader | 02.12.2026
Chris Mason is a man in a hurry.
“Sometimes walking from the subway to the lab takes too long, so I’ll start running,” he told me over breakfast at a bistro near his home in Brooklyn on a crisp...
By Katrina Miller, The New York TImes | 02.05.2026
Joseph Yracheta: The Native Biodata Consortium is the first nonprofit data and sample repository within the geographic bounds and legal jurisdiction of an American Indian nation, on the Cheyenne River Sioux Reservation in Eagle Butte, S.D.
NativeBio participated in a ...
By David Jensen, California Stem Cell Report | 02.10.2026
Touchy issues involving accusations that California’s $12 billion gene and stem cell research agency is pushing aside “good science” in favor of new priorities and preferences will be aired again in late March at a public meeting in Sacramento.
The...
By Lauren Hammer Breslow and Vanessa Smith, Bill of Health | 01.28.2026
On Jan. 24, 2026, the New York Times reported that DNA sequences contributed by children and families to support a federal effort to understand adolescent brain development were later co-opted by other researchers and used to publish “race science”...