This Company Wants to Rewrite the Future of Genetic Disease—Without Crispr Gene Editing
By Megan Molteni,
Wired
| 07. 07. 2020
Tessera Therapeutics is developing a new class of gene editors capable of precisely plugging in long stretches of DNA—something that Crispr can’t do.
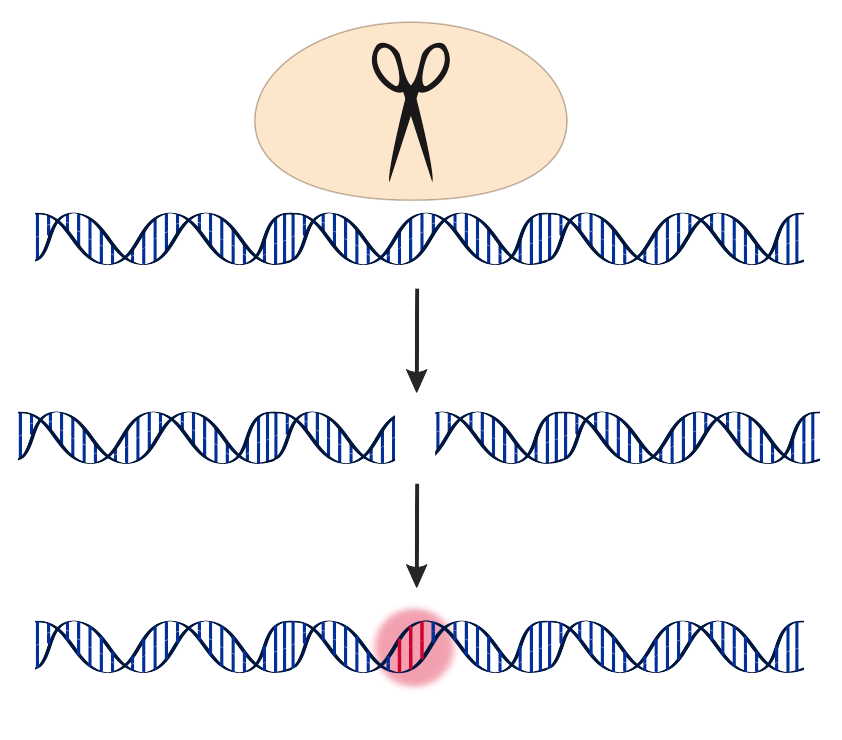
CRISPR’S POTENTIAL FOR curing inherited disease has made headlines, including at WIRED, for years. ( Here, here, here, and here.) Finally, at least for one family, the gene-editing technology is turning out to deliver more hope than hype. A year after 34-year-old Victoria Gray received an infusion of billions of Crispr’d cells, NPR reported last week that those cells were still alive and alleviating the complications of her sickle cell disease. Researchers say it’s still too soon to call it a cure. But as the first person with a genetic disorder to be successfully treated with Crispr in the US, it’s a huge milestone. And with dozens more clinical trials currently in progress, Crispr is just getting started.
Yet for all its DNA-snipping precision, Crispr is best at breaking DNA. In Gray’s case, the gene editor built by Crispr Therapeutics intentionally crippled a regulatory gene in her bone marrow cells, boosting production of a dormant, fetal form of hemoglobin, and overcoming a mutation that leads to poor production of the adult form of the oxygen-carrying molecule...
Related Articles
By Scott Solomon, The MIT Press Reader | 02.12.2026
Chris Mason is a man in a hurry.
“Sometimes walking from the subway to the lab takes too long, so I’ll start running,” he told me over breakfast at a bistro near his home in Brooklyn on a crisp...
By Diaa Hadid and Shweta Desai, NPR | 01.29.2026
MUMBRA, India — The afternoon sun shines on the woman in a commuter-town café, highlighting her almond-shaped eyes and pale skin, a look often sought after by couples who need an egg to have a baby.
"I have good eggs,"...
By George Janes, BioNews | 01.12.2026
A heart attack patient has become the first person to be treated in a clinical trial of an experimental gene therapy, which aims to strengthen blood vessels after coronary bypass surgery.
Coronary artery bypass surgery is performed to treat...
By Staff, ScienceDaily | 01.05.2026
Scientists at UNSW Sydney have developed a new form of CRISPR technology that could make gene therapy safer while also resolving a decades-long debate about how genes are switched off. The research shows that small chemical markers attached to DNA
...