Aggregated News
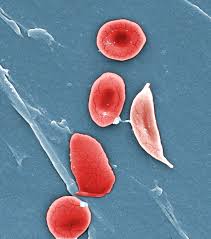
For the first time, doctors in the U.S. have used the powerful gene-editing technique CRISPR to try to treat a patient with a genetic disorder.
"It is just amazing how far things have come," says Victoria Gray, 34, of Forest, Miss. "It is wonderful," she told NPR in an exclusive interview after undergoing the landmark treatment for sickle cell disease.
Gray is the first patient ever to be publicly identified as being involved in a study testing the use of CRISPR for a genetic disease.
"I always had hoped that something will come along," she says from a hospital bed at the Sarah Cannon Research Institute in Nashville, Tenn., where she received an infusion of billions of genetically modified cells. "It's a good time to get healed."
But it probably will take months, if not years, of careful monitoring of Gray and other patients before doctors know whether the treatment is safe and how well it might be helping patients.
Sickle cell affects millions of people around the world. About 100,000 are in the U.S., and most of them...



